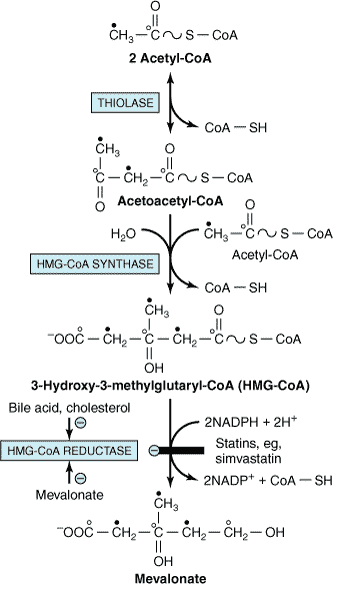
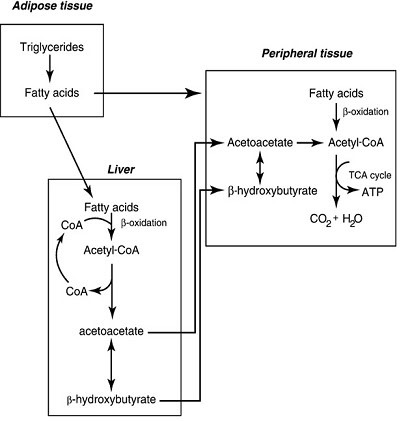
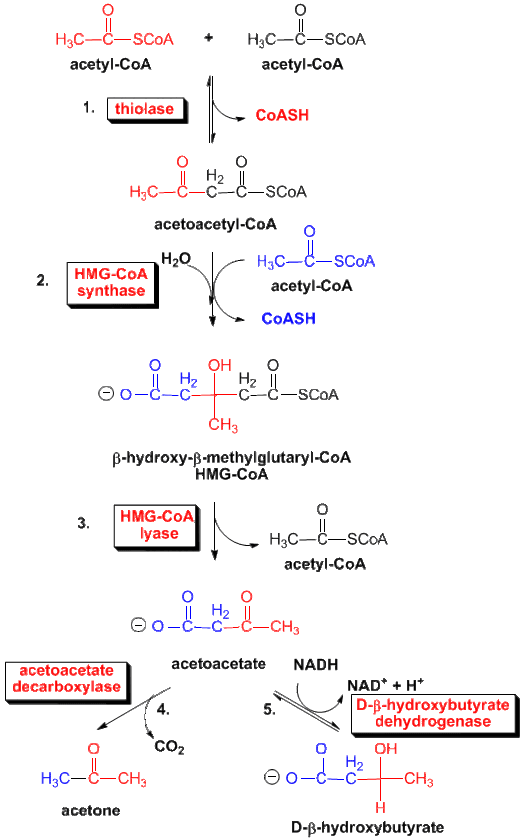
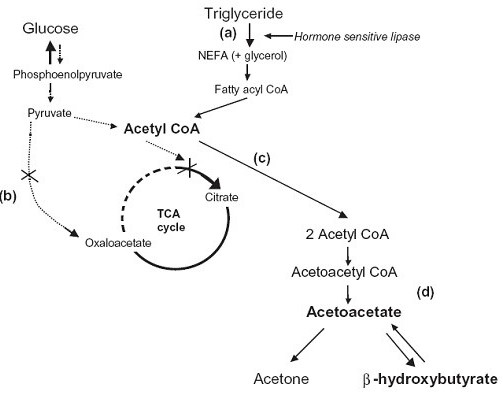
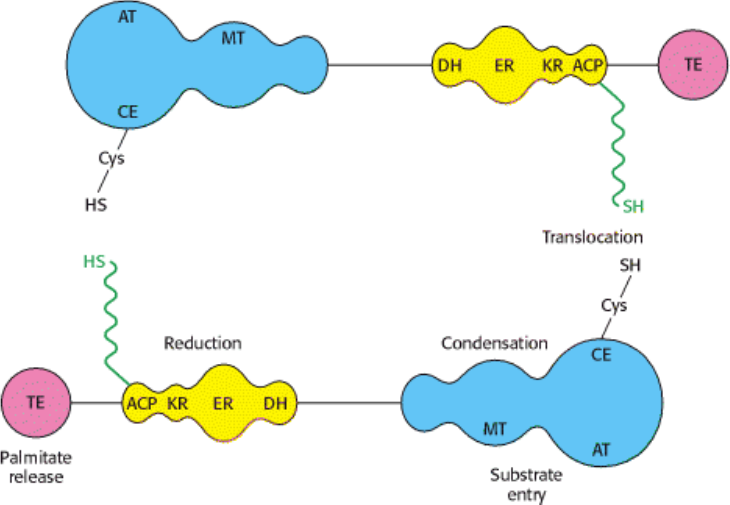
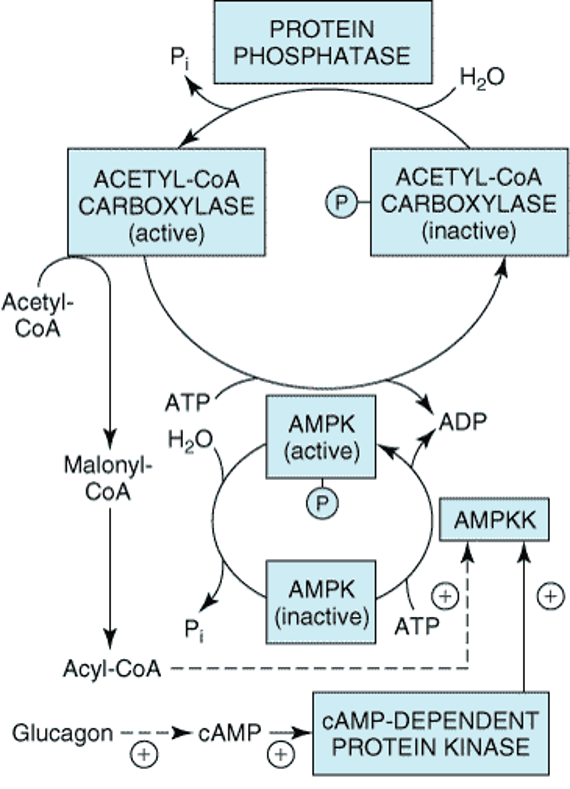
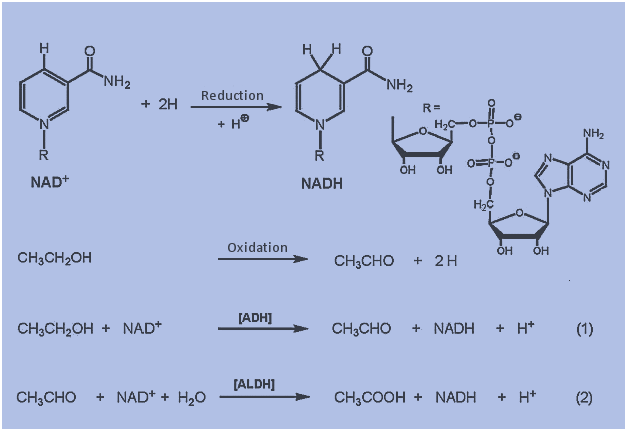
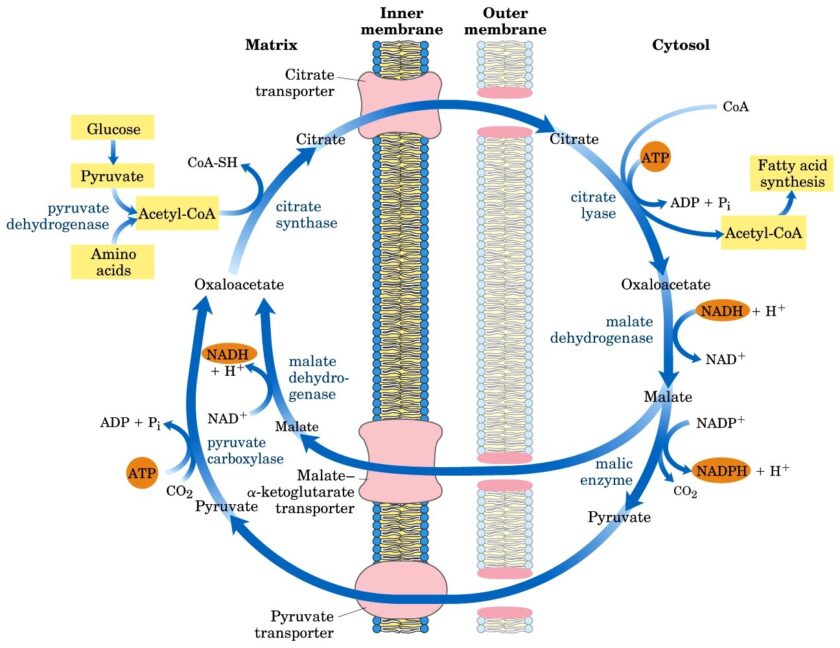
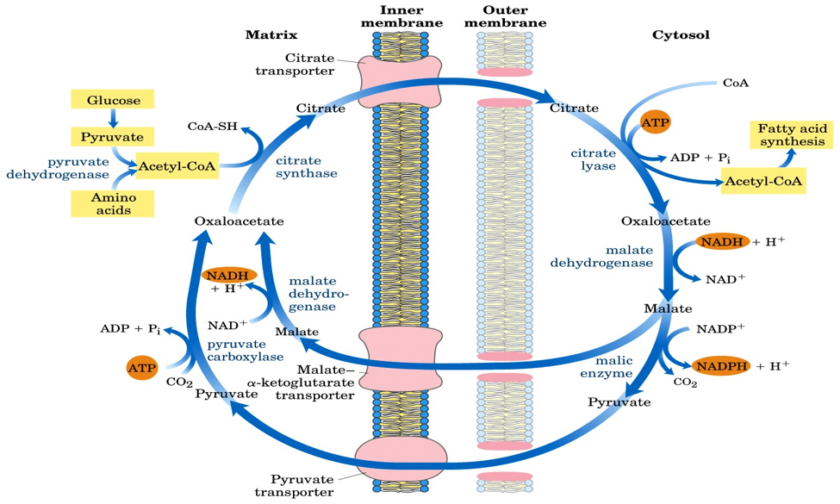
Steps of de novo synthesis of cholesterol
Steps of de novo synthesis of cholesterol Cholesterol is derived from diet, de novo synthesis, and the hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters. A little more than half the cholesterol in the body arises by synthesis (about 700 mg/d), and the average diet provides the remainder. The liver and intestine account for approximately 10% each of the […]