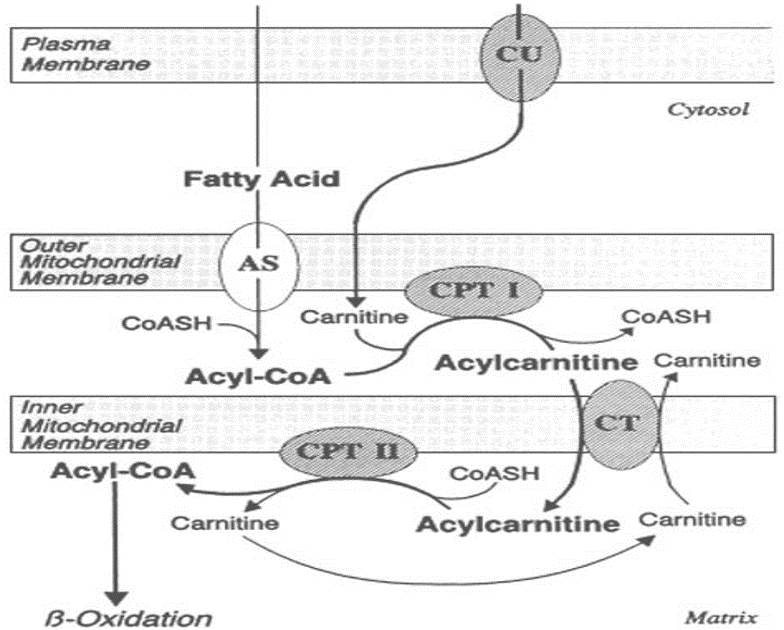
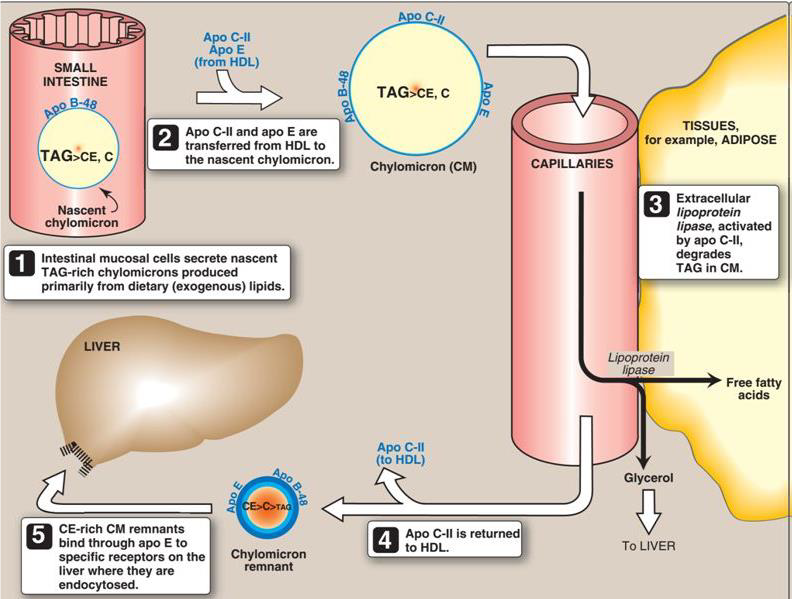
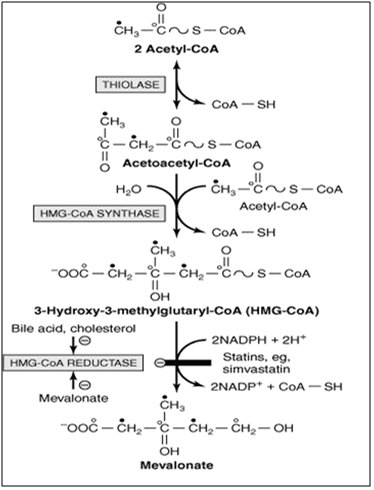
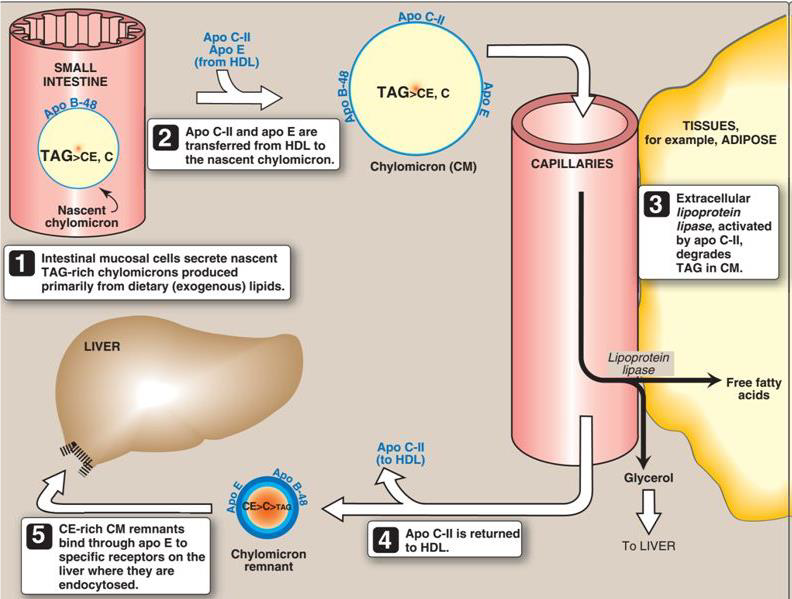
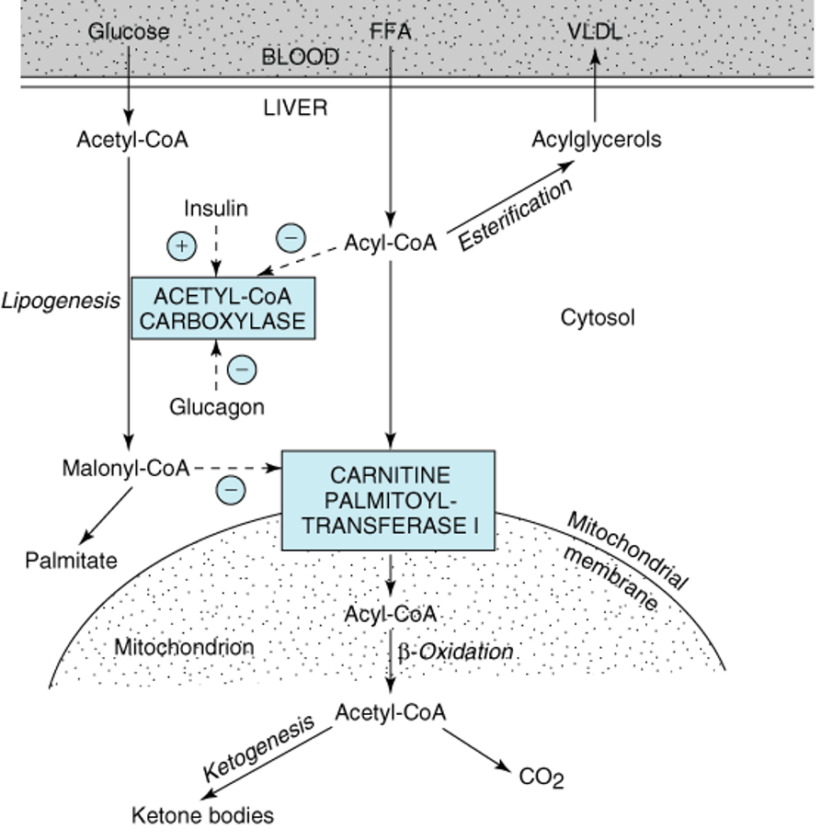
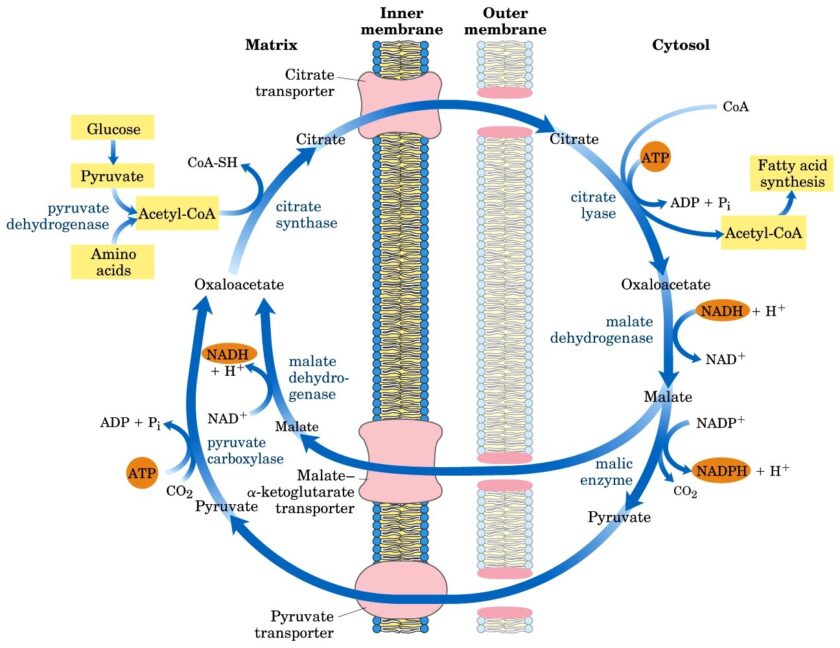
Essential Vitamins in Metabolism: Impacts on Fatty Acid, Triglyceride, and Nucleotide Pathways
“Discover how essential vitamins like B2, B3, B6, B12, folate, and others impact fatty acid, triglyceride, and nucleotide metabolism. This detailed overview explains impaired reactions, enzymes affected, and consequences of deficiencies.”