“Clinical Biochemistry: Fatty Acid Metabolism, Ketogenesis, and Energy Regulation”
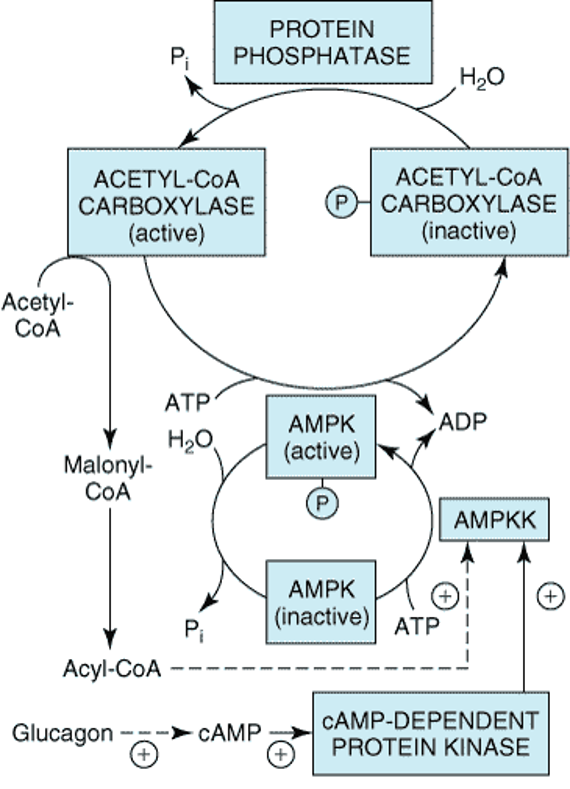
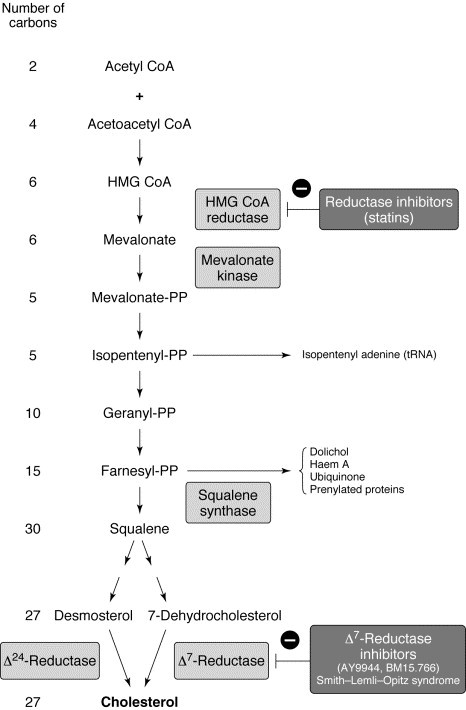
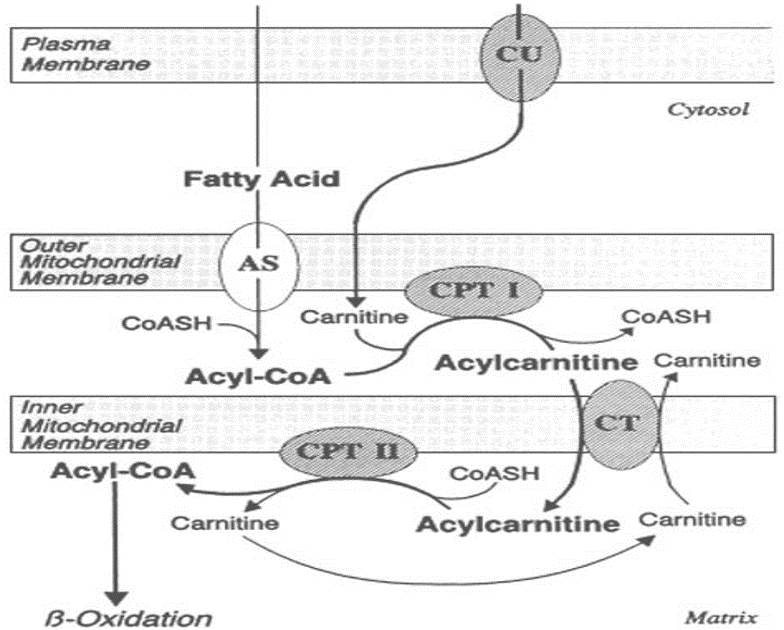
“Discover key insights into fatty acid metabolism, ketogenesis, and triglyceride synthesis through clinical scenarios. This guide explains enzyme deficiencies like MCAD, hormonal regulation by insulin, and the role of beta-oxidation and omega oxidation pathways in energy production.”
“Clinical Biochemistry: Fatty Acid Metabolism, Ketogenesis, and Energy Regulation” Read More »